The male reproductive ducts play a critical role in fertility and overall reproductive health. These ducts are responsible for transporting sperm from the testes to the urethra, where ejaculation occurs. Unfortunately, these ducts can sometimes experience blockages or disorders that severely impact fertility. Some of the most common conditions affecting these ducts include clogged ejaculatory ducts, male ejaculation blockages, and vas deferens obstruction symptoms. Understanding these issues is essential for men who are seeking to resolve them and restore their reproductive function.
For a deeper understanding of male infertility issues, refer to our comprehensive guide on male infertility assessment, which highlights the initial steps involved in identifying blockages.
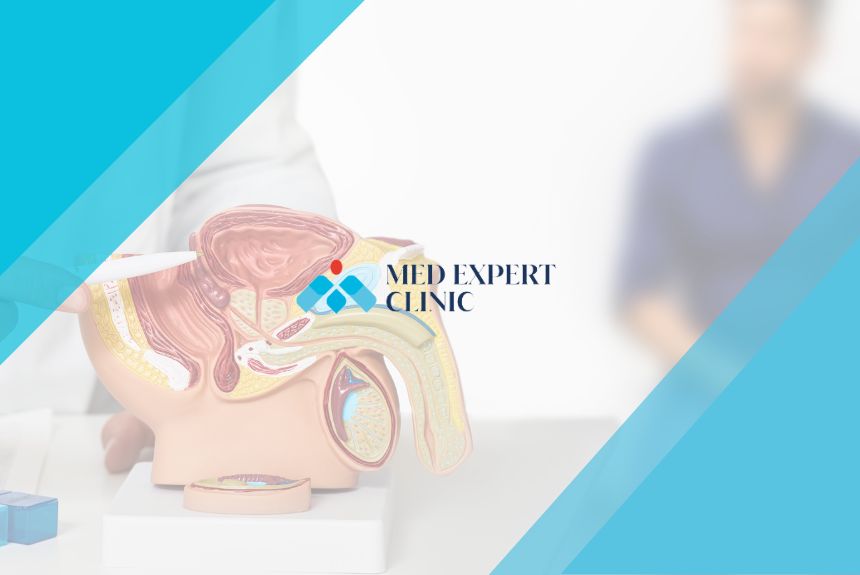
Understanding the Male Reproductive Ducts
The male reproductive ducts are a network of tubes responsible for the transport of sperm from the testes to the outside of the body during ejaculation. These ducts include:
- Vas deferens: The tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts.
- Ejaculatory ducts: Located within the prostate, these ducts are formed by the union of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicles, carrying sperm into the urethra.
- Seminal vesicles: Glands that produce a significant portion of the seminal fluid, which nourishes and protects sperm.
Each of these ducts plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. Any disruption, blockage, or damage to these structures can hinder sperm transportation, resulting in fertility challenges.
Functions of Seminal Fluid and Its Pathway
The seminal fluid, produced by the seminal vesicles and other glands, carries and nourishes sperm. This fluid travels through the male reproductive ducts, combining with sperm in the ejaculatory ducts. From there, the mixture of sperm and seminal fluid is expelled during ejaculation. If any part of this pathway is obstructed, it can prevent sperm from reaching the outside of the body, leading to male infertility.
Common Disorders and Blockages
Male Ejaculation Blockages
One common issue that affects the male reproductive ducts is male ejaculation blockages. These blockages can occur due to inflammation, scar tissue, or physical abnormalities that obstruct the normal flow of sperm during ejaculation. This condition can cause a significant reduction in sperm count or even complete infertility.
Seminal Fluid Blockages
Seminal fluid blockages can also disrupt the male reproductive system. These blockages may be caused by infections, cysts, or congenital defects. When the passage of seminal fluid is obstructed, it can impact sperm motility and prevent the proper transport of sperm through the reproductive ducts.
It is important to recognize the symptoms and conditions that affect the male reproductive ducts to seek timely treatment and prevent long-term fertility issues.
What Causes a Blocked Sperm Duct?
Common Causes of Blockages
A blocked sperm duct, or obstruction in the male reproductive ducts, can be caused by various factors. These blockages disrupt the normal flow of sperm, leading to reduced fertility or complete infertility. Understanding the causes is essential for determining the appropriate treatment. Below are the most common causes of blockages in the male reproductive system:
- Congenital defects: Congenital malformations are one of the primary causes of blocked sperm ducts. Some men are born with structural abnormalities, such as the absence of the vas deferens, which is the tube responsible for transporting sperm from the testes. Another congenital issue is ejaculatory duct cysts, which form within the duct and prevent sperm from passing through. These defects are present from birth and often go undetected until fertility issues arise in adulthood.
- Infections and inflammation: Infections play a significant role in causing blockages within the male reproductive system. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can lead to scarring and narrowing of the ducts. Prostatitis, an infection or inflammation of the prostate, can also cause blockages in the ejaculatory ducts. Chronic infections often result in long-term damage to the ducts, making early diagnosis and treatment critical.
- Injury or trauma: Physical injury or trauma to the reproductive area can cause blockages in the male reproductive ducts. This might happen due to sports injuries, surgery, or accidents that damage the vas deferens or ejaculatory ducts. Scar tissue from surgery, especially procedures involving the groin or pelvic area, can lead to narrowing or obstruction of these essential pathways. Trauma can disrupt the smooth flow of sperm, resulting in fertility issues.
Seminal Fluid Blockage and Ejaculatory Duct Obstruction
Blockages in the male reproductive ducts, such as those in the ejaculatory ducts, significantly impact the transportation of sperm. These blockages prevent sperm from being properly mixed with seminal fluid, which is essential for fertility. When seminal fluid cannot flow freely through the ducts, sperm remains trapped or fails to reach the urethra during ejaculation. This obstruction is a common cause of male infertility.
The ejaculatory ducts are located within the prostate, and their function is to carry sperm and seminal fluid from the vas deferens and seminal vesicles to the urethra. If these ducts become blocked, either by cysts, inflammation, or scar tissue, the normal process of ejaculation is disrupted. Men with this condition often produce very little semen, or in some cases, no semen at all. This significantly reduces the chances of natural conception.
In addition to fertility challenges, blocked ejaculatory ducts can cause other health problems, such as discomfort, pain, and an increased risk of infection. Since seminal fluid provides nutrients and protection for sperm, its obstruction also affects the quality of sperm, further complicating efforts to conceive.
Symptoms of Blockages in the Male Reproductive Ducts
Vas Deferens Obstruction Symptoms
The vas deferens plays a vital role in the transportation of sperm from the testes to the ejaculatory ducts. When there is an obstruction in this duct, several symptoms can indicate a problem. One of the most common symptoms is low semen volume. Men with vas deferens obstruction often produce less seminal fluid during ejaculation because sperm cannot reach the urethra.
Another sign of vas deferens obstruction is azoospermia, which is the complete absence of sperm in the semen. This condition can only be diagnosed through a semen analysis. Men with vas deferens obstruction may also experience pelvic discomfort or pain in the testicular region. These symptoms warrant further investigation by a medical professional.
Clogged Ejaculatory Duct Symptoms
A clogged ejaculatory duct can cause a range of uncomfortable and concerning symptoms. One of the most prominent signs is painful ejaculation, which can occur because the blocked duct prevents the normal release of semen during ejaculation. Men with clogged ducts may also notice low or no ejaculation. In some cases, the amount of semen produced is drastically reduced, or ejaculation does not occur at all.
Additionally, men with clogged ejaculatory ducts may experience blood in the semen. This condition, known as hematospermia, can be alarming and may indicate a serious issue with the reproductive ducts. Any of these symptoms should prompt a medical consultation, as they may indicate blockages that require treatment.
For more information on identifying blockages and other fertility issues, it is essential to undergo a semen analysis before IVF. This diagnostic test helps determine the cause of male infertility and offers valuable insights into the health of the reproductive system.
How Does Sperm Blockage Occur?
The Sperm Transport Pathway
The process of sperm transport begins in the testes, where sperm is produced. From there, sperm moves into the epididymis, a coiled tube where it matures and gains the ability to swim. Once matured, sperm travels through the vas deferens, a long muscular tube that carries it towards the ejaculatory ducts. During ejaculation, sperm combines with seminal fluid produced by the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. This mixture then travels through the ejaculatory ducts and is expelled through the urethra.
Blockages can occur at various points along this pathway, hindering the smooth transport of sperm. Obstructions in the vas deferens, epididymis, or ejaculatory ducts can prevent sperm from being mixed with seminal fluid or even reaching the urethra. Blockages in these areas can lead to fertility problems, as sperm is either absent from the semen or present in very low quantities, reducing the chances of conception.
Ejaculatory Duct Obstruction Mechanism
The ejaculatory ducts play a crucial role in the final stage of sperm transport. These ducts are located within the prostate and act as a passage for sperm and seminal fluid to exit the reproductive system. When the ejaculatory ducts become blocked, seminal fluid and sperm cannot pass through effectively, leading to a condition known as ejaculatory duct obstruction.
This blockage can be caused by cysts, inflammation, or scar tissue from previous infections. As a result, men may experience very low semen volume, pain during ejaculation, or even complete absence of semen. Blocked ejaculatory ducts are a common cause of male infertility, as sperm is unable to reach the outside of the body, making natural conception difficult or impossible.
Learn more about sperm transport issues and their effects on fertility.
Can You Fix a Blocked Sperm Duct?
Treatment Options for Blocked Ducts
Several treatment options are available to fix blocked sperm ducts, depending on the cause and location of the blockage. Surgical interventions are often the most effective solutions, especially when physical obstructions are involved. Common surgical procedures include:
- Vasovasostomy: This procedure is commonly used for vasectomy reversals, but it can also repair blockages in the vas deferens. The surgeon reconnects the severed or blocked sections of the vas deferens to restore the flow of sperm.
- Transurethral resection of the ejaculatory ducts (TURED): TURED is a surgical procedure used to remove blockages from the ejaculatory ducts. This surgery can help clear obstructions caused by cysts or scar tissue, allowing sperm to pass through the ducts during ejaculation.
- Other surgical interventions: Depending on the location of the blockage, other surgeries may be recommended to remove obstructions in the epididymis or seminal vesicles.
In cases where the blockage is caused by an infection or inflammation, non-surgical treatments may be effective. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat infection-related blockages, while hormone therapy can help resolve blockages caused by hormonal imbalances. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and restore normal function in the reproductive ducts.
Assisted Reproductive Techniques
When surgery or non-surgical treatments are not successful, assisted reproductive techniques (ART) can help men with blocked sperm ducts achieve pregnancy. One of the most common methods is in vitro fertilization (IVF), combined with sperm extraction techniques like TESA (testicular sperm aspiration), MESA (microsurgical epididymal sperm aspiration), or PESA (percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration).
These procedures involve extracting sperm directly from the testes or epididymis. The sperm is then used in IVF, where it is combined with an egg in a laboratory setting. ART can be an effective solution for men with irreversible blockages, offering a way to achieve fatherhood without the need for surgical repair of the ducts.
How to Fix Sperm Blockage?
Surgical Repair of the Vas Deferens and Ejaculatory Ducts
When it comes to fixing sperm blockages, vasovasostomy is one of the most commonly performed surgeries. This procedure is used to reconnect the vas deferens when it has been severed or obstructed, restoring the flow of sperm. The success rate of this surgery is high, and many men can regain their fertility after the procedure.
For blockages in the ejaculatory ducts, TURED is the most effective treatment. This minimally invasive surgery involves removing the obstruction from the ducts, allowing sperm to pass through and be mixed with seminal fluid during ejaculation. These surgical repairs are often successful in restoring fertility, especially when the blockage is detected early.
Microsurgery for Severe Cases
In more severe cases of blockages, microsurgery may be recommended. Microsurgery involves using specialized techniques to repair delicate structures like the epididymis and vas deferens. This type of surgery is particularly useful for men with complex blockages or scarring in multiple areas of the reproductive ducts. The success rate of microsurgery is high, and it offers a solution for men who may not be candidates for standard surgical procedures.
Alternatives for Fertility Treatment
For men with irreversible blockages, in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) are excellent alternatives. ICSI involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg, bypassing the need for natural sperm transport. IVF and ICSI can be used in combination with sperm extraction techniques to achieve fertilization, even in cases where sperm cannot be released during ejaculation.
These advanced reproductive technologies provide hope for men with severe or untreatable blockages, allowing them to become biological fathers despite the challenges of their condition.
Preventing Blockages in the Male Reproductive Ducts
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in preventing blockages in the male reproductive ducts. One of the most important practices is avoiding sexually transmitted infections (STIs), as infections can lead to scarring and blockages. Using protection during sexual activity and regular STI screenings can reduce this risk significantly. Quitting smoking is also essential. Smoking negatively impacts overall reproductive health and contributes to the development of blockages in the ducts. Additionally, reducing exposure to environmental toxins, such as heavy metals and industrial chemicals, helps protect the reproductive system from damage.
Maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress can further enhance reproductive health. These healthy practices support optimal sperm production and reduce the likelihood of obstructions in the reproductive ducts.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early detection of reproductive duct blockages is critical for preventing long-term damage and fertility issues. A semen analysis is a key diagnostic tool that helps identify blockages by assessing sperm count, motility, and volume. Regular reproductive health check-ups are essential for detecting issues early, before they progress into more serious conditions. By identifying blockages early on, men have a higher chance of restoring their fertility with less invasive treatments.
Advanced diagnostic tests, including imaging studies and hormone evaluations, can provide further insights into the underlying causes of blockages. Prompt treatment is crucial in avoiding permanent damage to the reproductive ducts.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for blockages in the male reproductive ducts is vital for preserving fertility. Early detection and lifestyle changes can prevent blockages, while timely treatment offers the best chance for recovery. Consult the medical experts at Med Expert Clinic to receive a personalized diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your condition. Contact us today to take the first step toward safeguarding your reproductive health!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of blockages in the male reproductive ducts?
The main causes of blockages include congenital defects, infections such as STIs, and physical injury or trauma to the reproductive area. These factors can lead to scarring, cyst formation, or narrowing of the ducts, all of which can obstruct sperm flow and contribute to fertility issues.
Can a blocked sperm duct be treated?
Yes, blocked sperm ducts can often be treated through surgical procedures such as vasovasostomy or TURED (transurethral resection of the ejaculatory ducts). In some cases, non-surgical treatments like antibiotics for infections or hormone therapy can also help. Assisted reproductive techniques such as IVF combined with sperm extraction may be an option when surgery isn’t viable.
What are the symptoms of a blocked sperm duct?
Common symptoms of a blocked sperm duct include low semen volume, painful ejaculation, the absence of sperm in semen (azoospermia), and even blood in the semen. These symptoms may vary depending on where the blockage occurs along the reproductive ducts.
How can I prevent blockages in my reproductive ducts?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing blockages. Avoiding sexually transmitted infections (STIs), quitting smoking, and reducing exposure to environmental toxins all contribute to better reproductive health. Regular check-ups and semen analysis can help in early detection and treatment of potential blockages.
Is early diagnosis important for treating blockages in the male reproductive system?
Yes, early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment. Detecting blockages early through semen analysis and other diagnostic tests can prevent permanent damage to the reproductive ducts and increase the chances of successful treatment, whether through surgery or non-invasive methods.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.