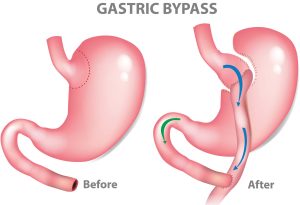
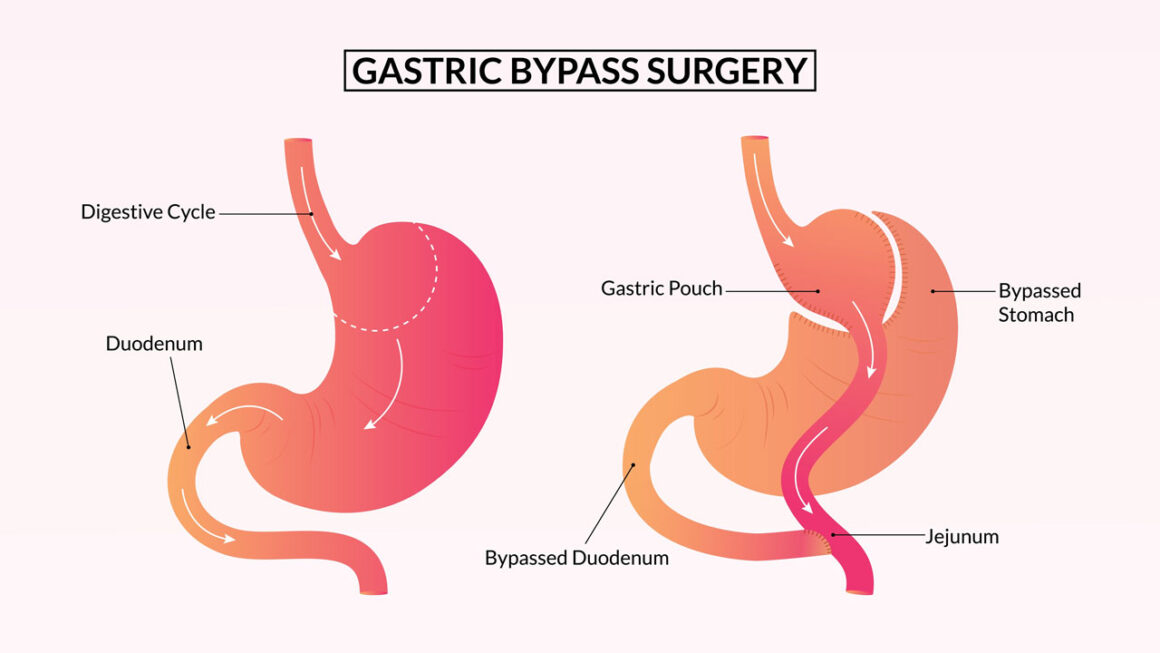
Gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y gastric bypass) is obesity surgery performed by removing a part of the stomach and connecting the new small stomach pocket (pouch) directly to the small intestine. Thus, both the stomach volume is reduced to 30-35 ml and a part of the small intestine is disabled in terms of nutrient absorption. In recent years, a much easier ‘mini gastric bypass’ technique has been introduced that can be applied in a shorter time causing less malabsorption. The difference with this new technique is that a slightly larger stomach volume is created.
 As a result of gastric bypass surgery, the amount of food taken decreases and some of the nutrients are excreted from the body without being absorbed.It is a surgery performed on extremely obese patients who cannot lose weight through diet and exercise. Serious weight loss can be achieved in the long term with gastric bypass surgery. How much weight loss is achieved depends on the type of surgery and lifestyle changes afterwards. It is possible to lose 70-100% of the excess weight at the end of two years.
As a result of gastric bypass surgery, the amount of food taken decreases and some of the nutrients are excreted from the body without being absorbed.It is a surgery performed on extremely obese patients who cannot lose weight through diet and exercise. Serious weight loss can be achieved in the long term with gastric bypass surgery. How much weight loss is achieved depends on the type of surgery and lifestyle changes afterwards. It is possible to lose 70-100% of the excess weight at the end of two years.
In addition, many health problems caused by excess weight are improved. In other words, it is actually a metabolic surgery. It improves your quality of life by providing improvement in reflux, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, heart disease, stroke, sleep apnoea and infertility problems.
In order for weight loss and the therapeutic effects that come with it to be permanent, it is very important to implement healthy lifestyle changes. Very close follow-up is required after this surgery. Eating habits should be changed and regular exercise should be a part of the rest of one’s life.
Absorption disorders due to surgery may cause some vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Therefore, regular vitamin and mineral support is required.
What is gastric bypass?
In gastric bypass surgery, a pocket is created from the stomach close to the oesophagus. Then this stomach pocket is connected to the small intestine by disabling a part of the small intestine close to the stomach (R&Y gastric bypass). In mini gastric bypass surgery, the stomach pocket is slightly larger.
What is treated with gastric bypass?
With gastric bypass surgery, patients can get rid of excess weight. Fat ratio decreases with weight loss; thus, metabolic diseases (such as type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension, sleep apnoea) improve.
Am I a suitable candidate for gastric bypass?
People with a body mass index (BMI)>40 or BMI>35 with at least one obesity-related disease such as type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension, sleep apnoea are suitable candidates for gastric bypass surgery.
What are the risks of gastric bypass surgery?
Risks such as bleeding, infection, fistula formation, embolism are also valid for this surgery.
 What should I do before gastric bypass surgery?
What should I do before gastric bypass surgery?
Detailed blood tests and endoscopy are performed before the operation. The patient is evaluated by the anaesthesiologist. If the patient is suitable for surgery, the operation is performed. Eating, drinking, smoking and the use of certain medications are restricted before surgery.
Step by step operation process
Anaesthesia: General anaesthesia is applied.
Surgical procedure: In gastric bypass surgery, a pocket is created in the stomach close to the oesophagus and then the small intestine is connected to this stomach pocket (R&Y gastric bypass, mini gastric bypass). Thus, part of the small intestine is bypassed in the absorption of nutrients.
What should I pay attention to after gastric bypass surgery?
The patient is discharged on the 2nd day after the operation and can return to normal activities. However, you should follow the diet recommended by your physician. The wound healing process is 3 weeks. During this period, watery food is consumed.
What are the results of gastric bypass surgery?
Since gastric bypass surgery has a reducing effect on nutrient absorption, it causes more weight loss than sleeve gastrectomy surgery. 70-100% of the excess weight can be lost. In addition, all weight-related metabolic diseases (such as type 2 diabetes, sleep-apnoea syndrome, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension) are improved. However, the rate of weight regain can reach 30-40% in people who do not apply the recommended lifestyle changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Gastric bypass surgery is an operation in which a small pocket is created in a region of the stomach close to the oesophagus and this stomach pocket is connected to the small intestine by disabling the first part of the small intestine that comes after the stomach (R&Y gastric bypass). In mini gastric bypass surgery, the stomach pocket created is slightly larger.
General surgeons experienced in bariatric surgery perform gastric bypass surgery.
People with BMI>40 or BMI>35 with at least one obesity-related disease such as type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension, sleep apnoea are suitable candidates for gastric bypass surgery.
People with BMI <35, alcohol addiction, psychological problems, eating disorders and those whose general health condition is not suitable for general anaesthesia cannot undergo gastric sleeve surgery.
Gastric bypass works in several ways. Because the newly created stomach pocket is smaller, it can hold less food, which means fewer calories are taken in. In addition, absorption is reduced because the food does not come into contact with the first part of the small intestine. Moreover, gastric motility is increased, allowing food to pass through the stomach and intestines faster. Thus, food absorption decreases and the amount of calories taken decreases. Most importantly, changing the flow of food through the digestive system has a powerful effect on reducing hunger, increasing satiety and enabling the body to reach and maintain a healthy weight.
The operation time is 60-90 minutes.
The patient is discharged in 2 days and can return to normal life in a week. Wound healing occurs in 3 weeks.
Full recovery takes 9-12 weeks.
Home rest is recommended for one week after gastric bypass surgery.
You can start working 2-3 weeks after the operation.
Postoperative pain lasts for one day.
Ibuprofen is one of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This group of drugs should be avoided as they can cause ulcers and irritation in the stomach.
Liquid food is consumed for one day after the operation. Starting from the 2nd day, you can switch to a semi-liquid diet. Additional vitamin and mineral support is given.
Protein, multivitamins, especially vitamin B12 and mineral supplements such as iron and calcium are recommended after surgery.
You should eat 4-6 times a day in small portions. You should eat slowly chewing food thoroughly and pureeing it before swallowing. Your diet should be rich in proteins. Do not drink water with meals. Instead, drink water 30 minutes before or after meals.
Gastric bypass is a very effective weight losing surgery as it causes decrease in nutrient absorption. As a result of long-term weight loss effect, 70-100% of excess weight can be lost. In addition, all weight-related metabolic disorderss (such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnoea, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension) are improved.
The effect of gastric bypass surgery on the hormonal system and the metabolic state of the body is so effective that it results in improvement of type 2 diabetes even before any weight loss. The operation also helps patients with reflux (heartburn) and often the symptoms improve rapidly. In addition, all weight-related metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnoea, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension are improved.
On the contrary, gastric bypass surgery prolongs life. It shows this effect by providing improvement in all weight-related metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnoea, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension, stroke.
Gastric bypass surgery is technically more complex and difficult than other weight losing operations. There is a risk of complications such as obstruction involving the small intestine. It causes more vitamin and mineral deficiency than sleeve gastrectomy. It can also cause “”dumping syndrome””, especially after sweet meals or drinks. There is a risk of developing ulcers, especially with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen or tobacco use.
In case of absolute necessity, reversal of the operation is possible, although complex and difficult.
Since the stomach pocket formed in gastric bypass surgery is a part of the upper part of the stomach that can stretch the least, it is not possible for this formed stomach pocket to enlarge and expand in the long term after surgery.
With gastric bypass, 70-100% of the excess weight can be lost. The rate of weight loss is faster than gastric sleeve surgery. However, the rate of weight regain is 15-20%.
The rate of weight regain can reach 30-40% in people who do not follow the recommended lifestyle changes.
It is important to have regular follow-ups so that your physician can follow the process and prevent weight gain in the long term. Carbonated and acidic drinks; rice, pasta and syrupy desserts should not be consumed for at least 2 years. Making the recommended lifestyle changes permanent will also make the weight loss and health improvement effect of the surgery permanent.
The most common complications of gastric bypass surgery are leakage through the sutures, ulcer development, Dumping syndrome and reflux.
After gastric bypass surgery, type 2 diabetes improves before weight loss begins. The operation also helps patients with reflux (heart burn) and often the symptoms improve rapidly. In addition, all weight-related metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnoea, hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension improve. Quality of life improves and life span is prolonged. However, since absorption problems are more common than other bariatric surgeries, vitamin and mineral supplementation is required.
Dumping syndrome is a condition seen after gastric bypass surgery, characterised by palpitations, sweating, weakness and fatigue caused by rapid emptying of the stomach.
After gastric bypass surgery, the stomach shrinks and its motility is increased resulting in a decrease in food absorption. This is the cause in the Dumping Syndrome that appears in two forms as ‘early’ and ‘late’ Dumping syndrome.
Early Dumping syndrome resolves spontaneously within 7-12 weeks. Late Dumping syndrome develops 1-3 hours after consuming food that has a very high sugar content. The body secretes excess insulin to absorb the high sugar content in the small intestine. As a result, blood sugar levels drop rapidly and at a high rate, causing complaints.
Sleeve gastrectomy is the most physiological obesity surgery method. In sleeve gasterectomy, since only the stomach is reduced and no intervention is made in the small intestines, the problem of absorption of nutrients is much less than in gastric bypass surgery. Therefore, Dumping syndrome seen in gastric bypass surgery is not seen in sleeve gastrectomy and postoperative vitamin and mineral deficiencies are less common. Due to the decrease in hunger hormone in sleeve gastrectomy, the amount of eating decreases in people who eat excessively large portions before surgery. The rate of weight loss in sleeve gastrectomy is slower than gastric bypass. Surgically, sleeve gastrectomy is an easier method. Therefore, complication rates are very low. However, it is an irreversible surgery. However, gastric bypass is a reversible surgical technique, although it has difficulties in case of absolute necessity.
Sleeve gastrectomy is the most physiological obesity surgery method.
Compared to gastric bypass surgery, mini gastric bypass surgery is an easier surgery. It causes less malabsorption because a larger stomach volume is created.
Mini gastric bypass surgery is especially suitable for people with type 2 diabetes, hypertension and a BMI>35.
Mini gastric bypass is a surgery performed in the treatment of metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension as well as weight loss.
The operation time is 60-90 minutes.
Liquid food is consumed for one day after the operation. Starting from the 2nd day, you can switch to a semi-liquid diet. Additional vitamin and mineral support is given. Protein, multivitamin, especially vitamin B12 and mineral support such as iron and calcium are recommended after surgery.
With mini gastric bypass, 70-100% of the excess weight can be lost within 1-2 years.
It is recommended to eat 800-1000 calories per day for the first 12-18 months and 1000-1200 calories per day after 18 months. You should avoid high-calorie and fatty foods and carbonated drinks. It is recommended to eat a protein-rich diet. You can consume 40-60 g of protein per day. You should drink 6-8 glasses of water a day.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.