Gastric balloon surgery is a minimally invasive weight loss procedure. It involves placing a balloon inside the stomach to reduce its capacity. As a result, patients feel fuller faster, which leads to weight loss. This procedure has become increasingly popular among those seeking non-surgical options for weight management.
The rise in obesity rates has driven the demand for alternative weight loss solutions. Unlike traditional surgical methods, gastric balloon surgery offers a less invasive approach with fewer risks. Patients can benefit from significant weight loss without the need for extensive surgery. This method appeals to those who may not qualify for or want to avoid more invasive procedures.
Understanding the intricacies of what is gastric balloon surgery is crucial for those considering this option. The procedure is tailored to individuals seeking effective weight loss without undergoing major surgery.
For more information on related weight loss procedures, you can read our detailed article on Bariatric Surgery: A Journey to a Healthier Life.
Understanding Gastric Balloon Surgery
What Is a Gastric Balloon?
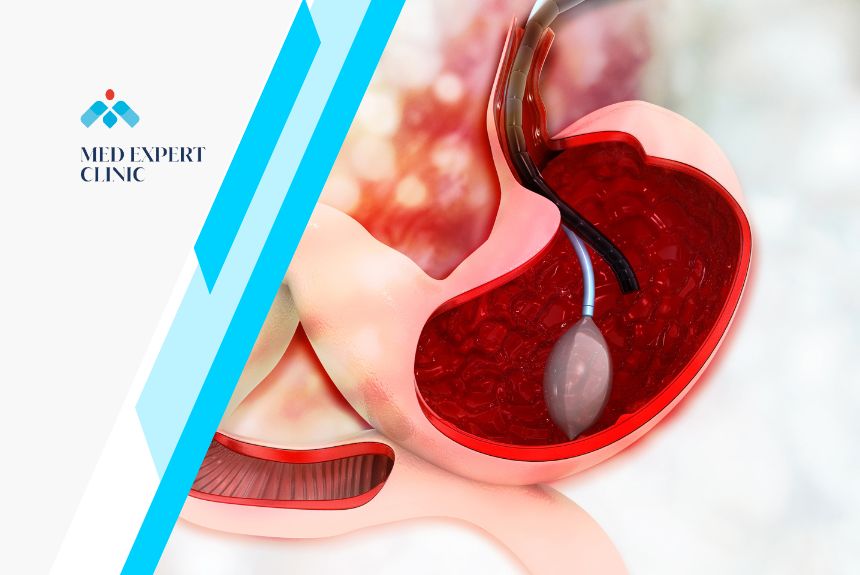
A gastric balloon is a soft, silicone balloon inserted into the stomach. Once in place, it is filled with saline or gas. The presence of the balloon limits the amount of food the stomach can hold, promoting a feeling of fullness.
The following are different types of gastric balloons:
- Orbera Balloon: A single balloon filled with saline, designed to stay in the stomach for up to six months.
- Allurion Balloon: A swallowable capsule balloon that does not require endoscopy for insertion or removal.
- ReShape Duo Balloon: Two connected balloons that offer more coverage in the stomach, intended for patients with a higher BMI.
How Does Gastric Balloon Surgery Work?
The gastric balloon procedure is a straightforward process. It begins with a consultation where the patient’s eligibility is assessed. If suitable, the procedure is scheduled. The balloon is then inserted into the stomach, typically via endoscopy or swallowing a capsule, depending on the type of balloon.
Here is an overview of the process:
- Consultation: The patient undergoes a thorough medical evaluation to determine if they are a good candidate for the procedure.
- Insertion: The balloon is inserted into the stomach either by swallowing a capsule or through endoscopy, depending on the balloon type.
- Adjustment Period: The patient adjusts to the presence of the balloon, which may include dietary changes and managing initial discomfort.
- Removal: After the designated period, usually 6 to 12 months, the balloon is removed in a similar manner to its insertion.
A comprehensive weight loss plan is essential alongside the gastric balloon. This plan includes diet, exercise, and behavioral changes to maximize the procedure’s effectiveness. The balloon alone is not a solution; it is a tool to aid in the overall weight loss journey.
Duration of the Gastric Balloon
The duration of the gastric balloon in the stomach varies depending on the type used. Generally, it lasts between 6 and 12 months. During this time, the patient can achieve significant weight loss. After the designated period, the balloon is removed, and patients are expected to continue with their weight management strategies.
The Procedure: How Is the Gastric Balloon Inserted?
Pre-Procedure Preparations
Before undergoing gastric balloon surgery, patients must follow several essential steps to ensure the procedure’s success. Preparation is crucial as it sets the foundation for a smooth insertion process and maximizes the balloon’s effectiveness in weight loss.
The following are key preparations patients should undertake:
- Medical Evaluation: Patients undergo a comprehensive medical assessment to evaluate their overall health and suitability for the procedure. This includes blood tests, imaging studies, and a review of medical history.
- Nutritional Counseling: A dietitian provides guidance on dietary adjustments needed before the procedure. This often involves adopting a low-calorie, low-fat diet to reduce the size of the liver, making the procedure safer and easier.
- Mental Health Support: Psychological evaluation and support are recommended to ensure patients are mentally prepared for the lifestyle changes required after the procedure.
- Medication Adjustments: Patients may need to stop or adjust certain medications, particularly those that affect blood clotting or interact with anesthesia.
- Fasting: Patients are usually required to fast for 12 hours before the procedure to ensure an empty stomach, which reduces the risk of complications during the insertion.
The Insertion Process
The insertion of the gastric balloon is a straightforward procedure that is typically completed within 20 to 30 minutes. It is minimally invasive and can be done on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how the balloon is inserted into the stomach:
- Administration of Sedation: The patient is given mild sedation or anesthesia to ensure comfort during the procedure. The type of sedation depends on the method of insertion.
- Insertion of the Balloon: Depending on the type of balloon, it is either swallowed as a capsule (as with the Allurion Balloon) or inserted endoscopically. For the endoscopic method, a thin tube with a camera is guided down the throat into the stomach.
- Balloon Inflation: Once in place, the balloon is filled with a saline solution or gas. The amount of filling is predetermined based on the patient’s specific needs and the type of balloon used.
- Final Check: After inflation, the balloon’s position is verified using imaging techniques. This ensures that it is correctly placed and functioning as intended.
- Recovery: The patient is monitored for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications. Once stable, they can return home to begin the adjustment period.
In cases where the Allurion Balloon is used, the process differs slightly. The patient swallows a capsule attached to a thin tube. Once the capsule reaches the stomach, it is inflated with gas, and the tube is removed without the need for endoscopy.
Post-Insertion Care
After the gastric balloon is inserted, patients can expect an adjustment period as their body adapts to the presence of the balloon. Immediate aftercare is critical for managing side effects and ensuring a successful outcome.
Initially, patients may experience nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort. These side effects are common as the stomach adjusts to the balloon. Medications are often prescribed to alleviate these symptoms. It’s essential to stay hydrated and follow the dietary guidelines provided by the healthcare team.
Dietary changes are a crucial aspect of post-insertion care. Patients are typically advised to start with a liquid diet for the first few days, gradually transitioning to soft foods, and eventually to regular meals. Portion control becomes vital, as overeating can cause discomfort or even damage the balloon.
In addition to dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments are necessary to maintain weight loss. Regular exercise, coupled with behavioral modifications, supports long-term success. Patients should also attend follow-up appointments to monitor their progress and make any necessary adjustments to their weight loss plan.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gastric Balloon Surgery
Benefits of Gastric Balloon Surgery
Gastric balloon surgery offers several benefits for those looking to lose weight. It is a non-surgical procedure that provides significant weight loss results, especially when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
The following are key benefits of gastric balloon surgery:
- Effective Weight Loss: Patients can lose a significant amount of weight, typically 10-15% of their total body weight, within the first six months.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure does not involve any incisions or stitches, reducing the risk of complications and speeding up recovery.
- Improved Health: Weight loss associated with the procedure can lead to improvements in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea.
- Temporary and Reversible: The balloon is removed after 6-12 months, offering a reversible option for weight loss without permanent changes to the digestive system.
Disadvantages and Risks
While gastric balloon surgery has many benefits, it is essential to consider the potential disadvantages and risks. Understanding these factors helps patients make informed decisions about their weight loss options.
Some of the main disadvantages and risks include:
- Temporary Solution: The balloon is a temporary device, which means weight loss must be maintained through lifestyle changes after its removal. There’s a risk of regaining weight if these changes are not sustained.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort, especially in the first few days after insertion.
- Balloon Complications: In rare cases, the balloon may deflate, leading to a blockage in the digestive system. This requires immediate medical attention.
- Limited Weight Loss: The amount of weight loss achieved with the balloon may be less than with more invasive procedures like gastric bypass surgery.
Is the Gastric Balloon Painful?
Many patients worry about the potential pain associated with gastric balloon surgery. While the procedure itself is not painful, the adjustment period can be uncomfortable. Most discomfort occurs in the first few days after insertion as the stomach adapts to the balloon’s presence.
The initial discomfort may include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps. These symptoms are usually temporary and can be managed with medication. Over time, as the body adjusts, these sensations typically subside.
Long-term pain is uncommon. However, patients should report any persistent or severe pain to their healthcare provider. Proper post-procedure care, including following dietary recommendations and attending follow-up appointments, can help minimize discomfort and ensure a smooth recovery.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Gastric Balloon Surgery?
Eligibility Criteria
Gastric balloon surgery is a suitable option for individuals who are struggling with obesity and have not achieved significant weight loss through diet and exercise alone. It is designed for those who need assistance in jumpstarting their weight loss journey. Candidates typically have a body mass index (BMI) between 30 and 40, which classifies them as obese.
In addition to BMI, other health conditions may qualify someone for this procedure. Patients with obesity-related comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea, are often considered good candidates. These conditions can be improved with weight loss, making the gastric balloon an effective intervention.
Potential candidates should also have a commitment to long-term lifestyle changes. The success of the procedure is heavily dependent on the patient’s willingness to adhere to dietary guidelines, engage in regular physical activity, and attend follow-up appointments. This dedication is crucial for sustaining weight loss after the balloon is removed.
Who Should Avoid It?
While gastric balloon surgery is a valuable tool for many, it is not suitable for everyone. Certain contraindications may disqualify individuals from undergoing the procedure. For example, those with a BMI lower than 30 may not benefit significantly from the surgery. Additionally, patients with severe gastrointestinal disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease or a history of gastric surgery, should avoid this treatment due to potential complications.
Individuals with psychological conditions that affect their relationship with food, such as eating disorders, are also not ideal candidates. The procedure requires significant behavioral changes that may be challenging for these patients. Moreover, those with severe liver disease, large hiatal hernias, or women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should not consider this option.
For those who are ineligible for gastric balloon surgery, alternative weight loss methods are available. These may include lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy, or other surgical interventions such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate approach based on individual circumstances.
Life After Gastric Balloon Surgery
Maintaining Weight Loss
Maintaining weight loss after gastric balloon surgery requires a strong commitment to healthy living. The balloon is only a temporary tool, and long-term success depends on the patient’s ability to sustain the habits developed during the balloon’s presence. Diet and exercise play a pivotal role in this maintenance phase.
Patients are encouraged to follow a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Portion control is essential, as overeating can stretch the stomach and negate the benefits of the procedure. Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or strength training, should be integrated into daily routines to support continued weight loss and overall health.
Regular follow-ups with the healthcare team are critical to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the weight loss plan. These appointments help identify potential challenges and provide ongoing support to ensure the patient stays on track. Adjustments to diet, exercise, or even behavioral therapy may be recommended based on individual needs.
Removal of the Gastric Balloon
The gastric balloon is typically removed after six to twelve months, depending on the type used and the patient’s progress. The removal process is straightforward and is usually done under mild sedation. If the balloon was inserted endoscopically, the removal is performed in a similar manner, with the balloon being deflated and then extracted through the mouth.
Patients should expect a brief recovery period following the removal. There may be mild discomfort, but most patients can resume normal activities within a day. After removal, it is crucial to continue adhering to the weight loss plan. The habits developed while the balloon was in place should be maintained to prevent weight regain. Ongoing support from healthcare providers can assist in this transition and reinforce healthy behaviors.
Summary of Gastric Balloon Surgery
Gastric balloon surgery offers a non-invasive option for individuals struggling with obesity, helping them achieve significant weight loss. The procedure is most effective for those with a BMI between 30 and 40 and can lead to improvements in obesity-related health conditions. However, it is important to remember that the gastric balloon is only a temporary solution. Long-term success depends on the patient’s commitment to a healthy lifestyle.
If you are considering gastric balloon surgery or exploring other weight loss options, it is crucial to consult with experienced healthcare professionals. They can guide you through the decision-making process and help you determine the best approach for your health needs. For more information on weight loss procedures, including gastric balloon surgery, visit our detailed guide on Bariatric Surgery: A Journey to a Healthier Life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gastric Balloon Surgery
What Is gastric balloon surgery?
Gastric balloon surgery is a non-invasive weight loss procedure where a silicone balloon is placed in the stomach to reduce its capacity, helping patients feel fuller faster and eat less. The balloon is temporary and usually remains in place for 6 to 12 months.
Who Is a good candidate for gastric balloon surgery?
Candidates for gastric balloon surgery typically have a BMI between 30 and 40 and have not achieved significant weight loss through diet and exercise alone. It is also suitable for individuals with obesity-related health conditions like type 2 diabetes or hypertension, provided they are committed to making long-term lifestyle changes.
How is the gastric balloon inserted and removed?
The gastric balloon is inserted either endoscopically or by swallowing a capsule, depending on the type of balloon. The procedure takes about 20 to 30 minutes and is done under mild sedation. The balloon is removed in a similar manner after 6 to 12 months, usually with mild sedation, and patients can typically resume normal activities within a day.
What are the benefits and risks of gastric balloon surgery?
The benefits of gastric balloon surgery include significant weight loss, a minimally invasive procedure, and improvements in obesity-related conditions. However, there are risks such as temporary side effects like nausea and vomiting, and potential complications like balloon deflation. It is important to weigh these factors when considering the procedure.
What should I expect after gastric balloon surgery?
After gastric balloon surgery, patients can expect an adjustment period with potential side effects like nausea and discomfort. Long-term success depends on maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise. Follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring progress and making any necessary adjustments to ensure sustained weight loss.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.