Uterine issues can significantly impact a woman’s fertility, making it challenging to conceive. These issues range from structural abnormalities to conditions like fibroids and endometriosis. Each of these conditions can interfere with conception, implantation, or carrying a pregnancy to term. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and types of uterine issues is essential for addressing fertility problems effectively.
When a woman experiences uterine issues, it can hinder her reproductive system’s ability to function properly. The uterus plays a crucial role in pregnancy. Any abnormalities or health concerns within it can have serious implications for fertility. Women facing uterine issues often experience symptoms like irregular periods, pelvic pain, or heavy bleeding. These symptoms can signal underlying problems that could affect their ability to conceive.
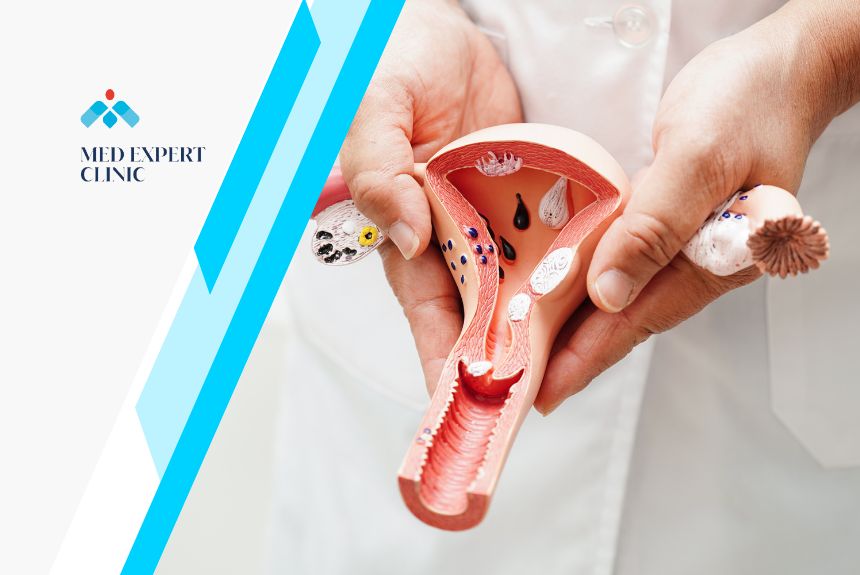
In many cases, uterine health is a key factor in determining a woman’s fertility. The uterus must be healthy for a fertilized egg to implant and grow. Issues within the uterus can prevent this process, leading to infertility. For example, conditions like Asherman’s Syndrome or fibroids can block the uterus or fallopian tubes, preventing conception. Without a healthy uterus, achieving a successful pregnancy becomes difficult, if not impossible.
It’s important for women to recognize the signs of potential uterine issues early. Timely diagnosis and treatment can improve fertility outcomes. By addressing these issues, women have a better chance of preserving their reproductive health. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare professionals are essential. Early detection of uterine issues can lead to better treatment options and increase the chances of conception.
For more information on assessing female infertility and understanding its causes, visit the Female Infertility Assessment Guide. This resource offers valuable insights into fertility assessments and the various factors that can influence a woman’s ability to conceive.
- Uterine issues are a major factor in female infertility.
- Structural abnormalities and other conditions can block conception.
- Symptoms like irregular periods may indicate underlying problems.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for fertility.
- Consulting with healthcare professionals can help address these issues effectively.
Understanding Uterine Issues and Infertility
Uterine issues encompass a variety of conditions affecting the uterus that can lead to infertility. These conditions may interfere with a woman’s ability to conceive or carry a pregnancy to term. The uterus plays a vital role in the reproductive system. Any abnormalities or health concerns in this organ can pose significant challenges to fertility. Recognizing these issues early is essential for addressing potential fertility problems effectively.
Many uterine issues can compromise fertility. They may prevent the fertilized egg from implanting, obstruct the fallopian tubes, or disrupt the uterus’s environment. When these issues are left untreated, they often become more severe, complicating treatment and reducing the chances of conception. That’s why timely diagnosis and treatment are so important. With prompt care, women can often manage or even overcome these challenges, preserving their fertility for the future.
There are various types of uterine issues that can impact fertility. These issues range from structural abnormalities to specific conditions like fibroids or endometriosis. Each condition affects the uterus differently, with varying symptoms and impacts on reproductive health. In some cases, the symptoms might be subtle, while in others, they may be more pronounced. Knowing the different types of uterine issues can help women identify potential signs early and seek appropriate medical care.
Types of Uterine Issues Affecting Fertility
Several common uterine issues, known as female issues with uterus, can lead to infertility. These include structural abnormalities, fibroids, endometriosis, and Asherman’s Syndrome. Understanding each of these conditions and their implications can aid in recognizing the need for medical intervention. Each issue presents unique challenges, but timely diagnosis can open doors to treatment options that improve fertility outcomes.
Structural Abnormalities
Structural abnormalities are physical irregularities in the uterus’s shape or size. These uterus related problems can affect how the uterus functions, leading to fertility issues. Common structural abnormalities include septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and uterine fibroids. Each anomaly affects the uterus differently, potentially obstructing conception or implantation.
- Septate Uterus: This condition occurs when a wall, or septum, divides the uterus into two sections. It may reduce the uterine cavity size, complicating implantation and increasing the risk of miscarriage.
- Bicornuate Uterus: With a bicornuate uterus, the organ has a heart-like shape with a significant indentation at the top. This shape can limit the uterus’s ability to expand, making it difficult to sustain a pregnancy.
- Uterine Fibroids: These are non-cancerous growths that develop within the uterine walls. They can obstruct the uterus, interfere with implantation, or block the fallopian tubes, impacting fertility.
Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are a common condition characterized by benign tumors that form within the uterine wall. Symptoms of uterus issues symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and frequent urination. Fibroids vary in size and number, and they can affect fertility by altering the shape of the uterus or blocking the passage of sperm. Large fibroids may even distort the uterus, making implantation difficult or impossible.
When fibroids grow in areas critical to conception, such as near the fallopian tubes or the uterine cavity, they can prevent a fertilized egg from implanting. Treatment options for fibroids include medication to reduce their size and, in severe cases, surgical removal. Early intervention can improve fertility outcomes and allow women to conceive without complications.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs. This tissue responds to hormonal changes, causing pain, inflammation, and scarring. Symptoms include severe menstrual cramps, chronic pelvic pain, and painful intercourse. Endometriosis can make it difficult for a fertilized egg to reach the uterus, complicating conception and increasing the risk of infertility.
Endometriosis often requires a combination of treatment options, including hormone therapy and surgery. For more information on this condition and its impact on fertility, you can read about the Challenges of Unexplained Infertility. Women with endometriosis frequently face unexplained infertility, which makes understanding and addressing this condition essential for fertility preservation.
Asherman’s Syndrome
Asherman’s Syndrome is a rare but serious uterine condition where scar tissue develops inside the uterus. This scarring can occur after surgery or infection, leading to adhesions that block the uterine cavity. Symptoms of Asherman’s Syndrome include light or absent menstrual periods and recurrent miscarriages. These adhesions can prevent a fertilized egg from implanting, causing infertility.
Diagnosing Asherman’s Syndrome often involves imaging tests like hysteroscopy, which allows doctors to view the uterine cavity. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the scar tissue and restore the uterus’s natural function. Timely intervention can improve fertility prospects, helping women affected by this condition to achieve successful pregnancies.
How Uterine Issues Lead to Infertility
Uterine issues can significantly interfere with a woman’s ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. These problems can affect several crucial stages of the reproductive process, including ovulation, fertilization, and implantation. Structural abnormalities, scarring, and conditions like fibroids can all alter the uterine environment, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant or for a pregnancy to progress. When uterine issues are present, the risk of infertility increases, often requiring medical intervention to resolve the underlying problem and improve fertility outcomes.
Various uterine issues can obstruct fertility. Conditions like endometriosis can cause inflammation and scarring, which interferes with the movement of sperm or eggs. Structural abnormalities, such as a septate uterus, can prevent the fertilized egg from properly implanting in the uterine wall. In many cases, uterine issues can also increase the likelihood of miscarriage, as the uterus may not be able to support a growing pregnancy. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential for addressing these issues and enhancing a woman’s chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy.
Cervical Damage and Infertility
Can a damaged cervix cause infertility? The cervix plays a crucial role in fertility by allowing sperm to pass from the vagina into the uterus. It also helps to keep the uterus closed during pregnancy to prevent premature labor. Damage to the cervix, whether from surgery, infection, or trauma, can interfere with its ability to perform these functions. For instance, cervical scarring or stenosis (narrowing of the cervix) can block the passage of sperm, reducing the chances of conception. In some cases, cervical damage may also result in an incompetent cervix, which can lead to recurrent miscarriages.
When the cervix is damaged, the quality of cervical mucus may also be affected, making it more difficult for sperm to swim through the cervix and reach the egg. If the cervix is unable to properly protect the uterus, infections may occur, further complicating the ability to conceive. For women with significant cervical damage, fertility treatments like intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be necessary to bypass the cervix and improve fertility outcomes.
Uterus Shape and Infertility
Can uterus shape cause infertility? The shape of the uterus is a key factor in determining a woman’s fertility. Abnormalities in uterine shape, such as a septate or bicornuate uterus, can interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg. In a septate uterus, a wall or septum divides the uterine cavity, reducing the space available for an embryo to implant and grow. This condition often leads to early miscarriages as the embryo may implant on the septum, which has poor blood supply and cannot support pregnancy.
A bicornuate uterus, where the uterus has two distinct sections, can also pose fertility challenges. This shape may limit the uterus’s ability to expand as the pregnancy progresses, increasing the risk of miscarriage or premature birth. In both cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct the uterine shape and improve the chances of a successful pregnancy. These uterine anomalies are often discovered during fertility evaluations, particularly when women experience recurrent miscarriages or unexplained infertility.
Common Uterine Anomalies Associated with Infertility
What is the most common uterine anomaly associated with infertility? The most frequent uterine anomalies affecting fertility are septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and fibroids. A septate uterus is the most common, with the septum dividing the uterine cavity and making it difficult for embryos to implant. A bicornuate uterus can also hinder pregnancy due to its irregular shape, which prevents normal fetal development.
- Septate Uterus: A condition where the uterine cavity is divided by a septum, reducing the space available for implantation.
- Bicornuate Uterus: A heart-shaped uterus that may not have enough space for the growing fetus, increasing miscarriage risks.
- Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths that develop within or around the uterus, potentially blocking the fallopian tubes or altering the shape of the uterine cavity.
These signs of uterus problems are critical to identify early, as they can prevent successful pregnancies or lead to recurrent miscarriages. Women experiencing these conditions should seek professional medical advice to explore treatment options and improve their chances of conception. For expert insights on fertility issues, visit the Expert Opinions on Fertility Issues.
Recognizing Symptoms of Uterine Issues
Recognizing the symptoms of uterine issues early is essential for preventing infertility. Common symptoms associated with uterine problems include abnormal menstrual cycles, heavy bleeding, severe pelvic pain, and recurrent miscarriages. Women with uterus issues symptoms may also experience pain during intercourse or frequent urination, particularly if fibroids are present.
Early recognition of these symptoms can lead to better diagnostic outcomes. The sooner uterine issues are detected, the more treatment options will be available to address them. Whether through surgery, medication, or lifestyle changes, addressing these problems promptly can help preserve fertility and increase the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
Recognizing Symptoms of Uterine Issues
Early recognition of uterus issues symptoms is vital for preventing infertility. Common symptoms of uterine problems include irregular menstrual cycles, heavy or prolonged periods, and severe pelvic pain. Women may also experience pain during intercourse or frequent urination, especially if fibroids are present. Recurrent miscarriages can also signal underlying uterine issues that might affect fertility.
Not all symptoms are obvious, and some may be subtle. A slight increase in menstrual pain or spotting between periods could indicate a problem. Pelvic pressure and bloating are additional signs to watch for, as they may suggest the presence of fibroids or other growths within the uterus. Recognizing these symptoms early provides an opportunity for timely intervention, which can improve fertility outcomes significantly.
- Heavy or irregular periods
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination
- Recurrent miscarriages
Seeking medical attention when these symptoms appear is essential. A healthcare provider can evaluate these signs and recommend diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause. Early diagnosis and treatment offer the best chance of resolving these issues before they impact fertility further.
Diagnosing and Treating Uterine Issues for Fertility
Accurate diagnosis is the first step in managing uterine issues related to infertility. Various tests and procedures help in identifying the exact nature of uterine problems. These tests provide crucial information that guides the treatment plan, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Diagnostic Tests for Uterine Issues
Several diagnostic tools are available to detect uterine issues. Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is one common test. It uses X-rays to check for blockages in the fallopian tubes and examines the shape of the uterus. An ultrasound provides detailed images of the uterus and ovaries, helping doctors identify fibroids, cysts, or other growths. For more detailed views, an MRI can offer high-resolution images of the uterus and surrounding structures, allowing for a more comprehensive assessment.
Each of these tests provides unique insights into uterine health. Together, they can help healthcare providers determine the best course of action for addressing uterine-related fertility issues. An accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the specific needs of the patient.
Treatment Options for Uterine-Related Infertility
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, several treatment options are available. Surgery may be necessary for structural abnormalities, such as a septate or bicornuate uterus, to improve fertility prospects. For conditions like fibroids, treatments may include hormonal therapy to shrink the growths or minimally invasive surgery to remove them.
Hormonal therapies can also manage endometriosis by reducing the growth of tissue outside the uterus. In some cases, in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended to bypass uterine or cervical issues entirely. For women with Asherman’s Syndrome, surgical removal of scar tissue can restore the uterine cavity, enhancing fertility. Treatment plans vary based on the individual’s condition, but early intervention offers the best chance for success.
Prevention and Lifestyle Considerations
Maintaining uterine health involves more than just medical treatment. Lifestyle factors can play a significant role in preventing uterine issues. Regular medical check-ups are crucial, as they help detect problems early before they affect fertility. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support reproductive health and reduce inflammation.
Exercise is another essential aspect of maintaining uterine health. Physical activity promotes blood circulation and helps maintain a healthy weight, which can reduce the risk of uterine problems. Stress management is equally important, as chronic stress can impact hormone levels and overall reproductive health. Simple lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in preserving fertility and uterine function.
Conclusion
Understanding and recognizing the symptoms of uterine issues is the first step toward preserving fertility. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential, as they can prevent complications and improve the chances of a successful pregnancy. Diagnostic tools like HSG, ultrasound, and MRI are invaluable for detecting uterine problems. Treatment options such as surgery and hormonal therapy offer hope for those facing these challenges.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking regular medical care, women can protect their reproductive health. If you have concerns about uterine issues or fertility, consult with a healthcare provider. Early intervention can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. For more information on managing uterine health and fertility, visit Med Expert Clinic to schedule a consultation and learn more about your options.
Frequently Asked Questions about Uterine Issues and Infertility
What are common symptoms of uterine issues that can impact fertility?
Common symptoms include irregular or heavy menstrual periods, severe pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, frequent urination, and recurrent miscarriages. Recognizing these signs early can help with timely diagnosis and treatment, improving fertility outcomes.
Can uterine fibroids cause infertility?
Yes, uterine fibroids can interfere with fertility by altering the shape of the uterus, blocking the fallopian tubes, or disrupting the implantation of a fertilized egg. Treatment options like hormonal therapy or surgery may help improve fertility in cases involving fibroids.
How do structural abnormalities in the uterus affect fertility?
Structural abnormalities, such as a septate or bicornuate uterus, can hinder the implantation and growth of an embryo. These conditions may increase the risk of miscarriage and, in some cases, require surgical correction to improve fertility prospects.
What diagnostic tests are used to detect uterine issues related to infertility?
Tests like hysterosalpingography (HSG), ultrasound, and MRI are commonly used to diagnose uterine issues. These tests provide detailed images and information that help doctors identify problems affecting fertility, such as fibroids or structural abnormalities.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help prevent uterine issues affecting fertility?
Yes, maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and scheduling routine medical check-ups can all support uterine health. These lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of uterine issues and improve overall reproductive health.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.