The gastric balloon has become increasingly popular as a non-surgical weight loss option for those seeking an effective way to manage weight. Unlike surgical procedures, this approach provides a minimally invasive solution that has shown significant success in helping individuals achieve their weight loss goals. However, like any medical intervention, the gastric balloon comes with potential side effects that users need to be aware of. Understanding the side effects of gastric balloon placement is crucial for anyone considering this option, as it allows them to make informed decisions about their health and safety.
In this article, we’ll explore the common side effects and complications associated with gastric balloon procedures. By examining each potential risk, readers can better understand how to prepare for the experience and manage any unexpected symptoms. For those just beginning their journey, our Before Gastric Balloon Placement Guide offers valuable insights into what to expect before the procedure.
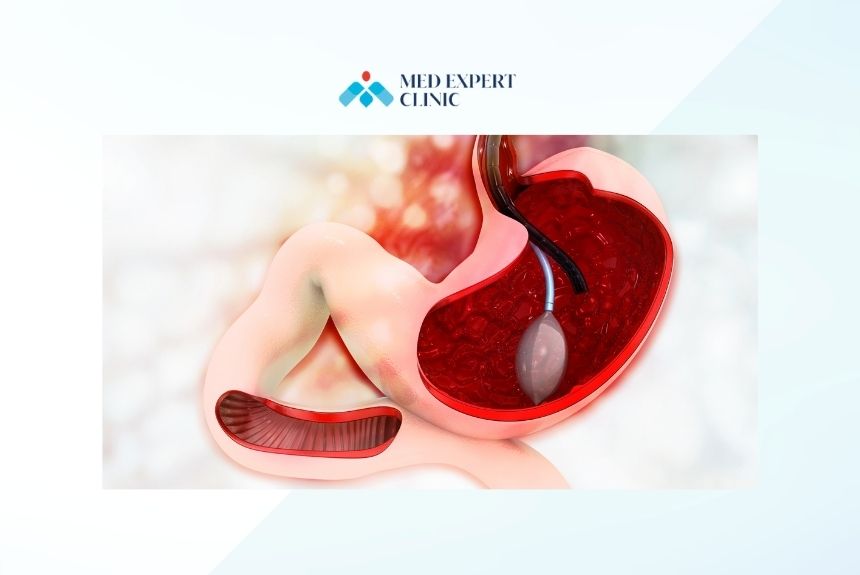
What is a Gastric Balloon and How Does It Work?
Purpose of the Procedure
The gastric balloon is a non-surgical weight loss tool designed to assist individuals in managing their weight by promoting feelings of fullness. Unlike traditional surgical methods, the gastric balloon procedure does not require incisions, making it an attractive choice for those seeking a less invasive option. This approach works as an aid rather than a permanent solution, helping users develop healthier eating habits and reach a more manageable weight range.
The gastric balloon works by occupying space in the stomach, which reduces the amount of food a person can consume in one sitting. This reduced capacity encourages smaller portion sizes and helps patients achieve a calorie deficit, ultimately promoting weight loss over time. For individuals struggling with portion control, the balloon can serve as an effective tool to improve eating habits and lead to lasting lifestyle changes. The method has been widely adopted for its simplicity and effectiveness, particularly among those looking for alternatives to surgical interventions.
Procedure Overview
The gastric balloon placement is a straightforward process performed under sedation. During the procedure, a deflated balloon is inserted through the mouth and guided into the stomach. Once in place, it is filled with a saline solution to expand and occupy a portion of the stomach. The entire procedure is typically completed within 20-30 minutes, allowing most patients to go home the same day.
Once the balloon is in place, patients often experience reduced hunger and feel full more quickly when eating. This satiety effect is the primary mechanism through which the weight loss balloon assists in weight management. By reducing food intake, individuals can achieve weight loss without the need for more invasive surgeries.
It’s important to note that the gastric balloon is a temporary solution and is usually left in the stomach for six months. During this period, patients work closely with their healthcare provider to adopt healthier eating and exercise habits. The goal is not only to lose weight but also to sustain these changes after the balloon is removed.
- Non-surgical and minimally invasive procedure, making it a popular choice.
- Promotes satiety by filling part of the stomach, helping to control portions.
- Encourages healthier eating habits over time through structured guidance.
- Temporary solution, typically lasting about six months.
- Provides support in achieving weight loss goals without surgical risks.
The non-surgical weight loss approach offered by the gastric balloon has shown promising results for many people. However, as with any medical procedure, it is essential to be aware of the side effects and take preventive steps where possible. This article will guide you through the key points to consider when assessing the benefits and potential challenges of the gastric balloon.
Common Side Effects of Gastric Balloon
1. Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are among the most common side effects following gastric balloon placement. Many patients experience these symptoms in the initial days as their bodies adjust to the presence of a foreign object in the stomach. The gastric balloon occupies space in the stomach, which can irritate the stomach lining, leading to sensations of nausea. This reaction is a normal response as the digestive system tries to adapt to the balloon, often mistaking it for food that needs to be digested.
For most individuals, nausea and vomiting lessen within the first week after the procedure. However, in some cases, these symptoms can persist for a longer period, making it challenging to maintain hydration and nutrient intake. To manage gastric balloon nausea, doctors often prescribe anti-nausea medications for use in the days following the procedure. Staying hydrated, eating small portions, and avoiding rich or greasy foods can also help alleviate nausea. Sipping ginger tea or peppermint tea, known for their natural soothing effects on the stomach, may also provide relief.
2. Abdominal Pain and Discomfort
Abdominal pain and discomfort are common side effects that many patients experience after gastric balloon placement. This discomfort is primarily due to the body adjusting to the balloon’s presence in the stomach. The stomach muscles may contract around the balloon, causing cramping or a sensation of pressure. This reaction is natural as the stomach attempts to process the presence of an unfamiliar object.
In most cases, the abdominal pain is mild and decreases as the body acclimates to the balloon. Patients may feel uncomfortable when they eat or drink, particularly if they consume larger portions. Over time, however, the body generally adapts, and the discomfort subsides. It’s essential to monitor the pain level. If it becomes severe or does not improve within a few days, it’s advisable to contact a healthcare provider. They may recommend pain relievers or suggest dietary adjustments to reduce discomfort. Reaching out to a doctor promptly is important to rule out any complications if the pain intensifies.
3. Acid Reflux and Heartburn
Acid reflux and heartburn are also common side effects experienced by patients with a gastric balloon. The balloon’s presence can exert pressure on the stomach’s internal walls, which may lead to an increase in acid production. As stomach acid moves up into the esophagus, it causes the familiar burning sensation associated with heartburn. The feeling can be uncomfortable, especially after meals.
To manage acid reflux, patients are often advised to eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of three large ones. This adjustment reduces the chance of overfilling the stomach, which can increase pressure and acid production. Additionally, avoiding spicy foods, acidic beverages, and caffeine can lessen the occurrence of acid reflux. Over-the-counter antacids can also help alleviate symptoms, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider if heartburn persists, as prolonged reflux can cause damage to the esophageal lining.
4. Bloating and Gas
Bloating and increased gas are common side effects for those with a gastric balloon. The balloon can interfere with normal digestion, causing gas to build up in the stomach. This effect can be uncomfortable and may lead to feelings of fullness or bloating, even with small meals. Some patients may also experience belching or a sensation of heaviness in the abdomen.
Simple dietary modifications can help manage bloating and gas. Patients are encouraged to avoid carbonated beverages, which can increase gas buildup, and to limit high-fiber foods in the initial days following the procedure. Eating slowly and chewing thoroughly can also prevent excess air from entering the stomach, which contributes to bloating. Small changes in eating habits can significantly reduce bloating, allowing for a more comfortable experience with the gastric balloon.
5. Constipation or Diarrhea
Changes in digestion, such as constipation or diarrhea, are also reported side effects of the gastric balloon procedure. The balloon’s presence can disrupt the normal movement of food and waste through the digestive tract. In some cases, the reduced stomach capacity may affect how efficiently the intestines process waste, leading to constipation. This effect can be uncomfortable and may require dietary changes to address.
Conversely, some patients experience diarrhea, often due to changes in diet and the digestive system’s adaptation to the balloon. To manage these symptoms, healthcare providers often recommend dietary adjustments tailored to the patient’s needs. Consuming more fiber-rich foods and drinking plenty of water can help alleviate constipation. For those experiencing diarrhea, it’s essential to stay hydrated and consider incorporating bland, easily digestible foods. By maintaining a balanced diet and following medical guidance, patients can usually overcome these temporary digestive changes.
- Nausea and vomiting are common immediately after placement but typically subside within the first week.
- Abdominal pain or cramping may occur as the body adjusts to the balloon.
- Acid reflux and heartburn can often be managed with dietary adjustments and smaller, frequent meals.
- Bloating and gas may arise due to digestion changes; reducing carbonated drinks can help.
- Constipation or diarrhea can result from dietary changes and may require fiber adjustments or hydration.
Understanding these common side effects allows patients to better prepare for their gastric balloon journey. Consulting with a healthcare provider and following recommended dietary adjustments can significantly reduce the impact of these side effects, promoting a smoother and more comfortable experience with the gastric balloon.
Recognizing Severe Gastric Balloon Complications
Gastric Balloon Deflation or Migration
While the gastric balloon procedure is generally safe, there is a potential risk of balloon deflation. If the balloon deflates, it can migrate through the digestive tract. This movement poses a significant health risk, as the deflated balloon could cause an obstruction. When the balloon moves into the intestines, it may lead to a blockage, which can be painful and require emergency intervention.
Patients should monitor their bodies for signs that could indicate deflation or migration. Key symptoms to watch for include intense abdominal pain, unexplained vomiting, and a general feeling of being unwell. These symptoms can develop suddenly and may worsen over time if left untreated. If any of these symptoms arise, it’s crucial to seek medical assistance promptly to prevent complications.
After the procedure, staying vigilant about potential complications is essential. For additional insights on how to maintain post-procedure awareness, visit our Life After Gastric Balloon Tips page. This resource provides helpful guidance on recognizing warning signs and maintaining a healthy recovery process.
Stomach or Esophageal Ulcers
Another severe complication associated with the gastric balloon is the development of stomach or esophageal ulcers. The balloon exerts constant pressure on the stomach lining, which, in some cases, can irritate the tissue and lead to ulcer formation. This condition is rare but can occur, particularly if the balloon causes friction against the stomach or esophagus walls.
Ulcers in these areas can cause significant discomfort and may lead to additional complications if not addressed promptly. Patients should be mindful of the following symptoms, which may indicate the presence of an ulcer:
- Persistent Stomach Pain: A constant ache or sharp pain in the stomach that doesn’t subside.
- Discomfort When Eating: Pain or discomfort that intensifies during meals.
- Potential Bleeding: Vomiting blood or noticing dark stools, which may signal bleeding ulcers.
If any of these symptoms are present, it’s crucial to contact a healthcare provider to assess the condition. Ulcers can usually be treated with medication, but in some cases, they may require additional medical intervention.
Gastric Balloon Infection
Though rare, infections can develop as a complication of the gastric balloon procedure. Infections occur when bacteria enter the stomach lining or surrounding tissues, potentially leading to severe health issues. Recognizing the symptoms of gastric balloon infection is essential for early detection and treatment.
Common signs of infection include:
- Fever: Elevated body temperature may indicate the presence of an infection.
- Chills: Experiencing chills or sudden temperature changes could be a response to infection.
- Abdominal Pain: Pain that worsens, especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
If any of these symptoms occur, it’s vital to contact a healthcare provider immediately. Infections can escalate quickly, so early medical attention is crucial to prevent further complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Gastric Balloon Side Effects
Knowing when to seek medical attention is essential for anyone who has undergone a gastric balloon procedure. Some symptoms should never be ignored, as they may indicate severe complications. If you experience any of the following signs, reach out to a healthcare provider without delay:
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Intense or persistent pain that doesn’t improve.
- Fever: Elevated temperature, especially if accompanied by other symptoms.
- Persistent Vomiting: Ongoing vomiting that prevents hydration and nutrient intake.
- Difficulty Breathing: Any breathing issues require immediate medical evaluation.
Taking a proactive approach to health is essential. If you notice any unusual symptoms or feel concerned about your recovery, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from becoming serious health threats.
For a broader perspective on the benefits of gastric balloon procedures and how they support weight loss, visit our Benefits of Gastric Balloon for Weight Loss page. This resource highlights the positive aspects of the procedure and helps balance the discussion around potential complications with the positive outcomes many patients experience.
Managing and Minimizing Risks of Gastric Balloon Side Effects
1. Following a Recommended Diet
Following a carefully structured diet is essential to reduce the risk of side effects like nausea and acid reflux after a gastric balloon placement. Patients are typically advised to start with liquids and slowly progress to soft foods before resuming a regular diet. Avoiding heavy, greasy, or spicy foods can significantly reduce nausea, as these foods tend to irritate the stomach. Small, frequent meals are generally recommended to prevent acid reflux, as eating too much at once may increase pressure on the stomach, leading to discomfort.
Additionally, choosing bland and easily digestible foods during the initial weeks can help the body adapt to the balloon. Many patients find that foods like oatmeal, bananas, and rice are gentle on the stomach. Adhering to a recommended diet helps minimize irritation and supports a smoother recovery, allowing the balloon to aid in weight loss without causing unnecessary discomfort.
2. Maintaining Regular Medical Follow-Ups
Regular medical follow-ups play a crucial role in monitoring the success of the gastric balloon procedure and managing any side effects early on. These appointments allow healthcare providers to evaluate the patient’s progress, adjust dietary or lifestyle recommendations, and address any emerging side effects. Early detection of complications, such as balloon migration or excessive discomfort, is critical to ensure patient safety and long-term health benefits.
Through routine check-ins, doctors can also provide additional guidance to help patients achieve optimal weight loss results. Consistent follow-ups reinforce healthy habits and provide patients with the reassurance that any concerns will be addressed quickly, supporting a successful outcome.
3. Staying Hydrated and Practicing Mindful Eating
Staying hydrated is fundamental for anyone with a gastric balloon, as dehydration can worsen side effects like nausea and dizziness. Patients should aim to sip water throughout the day rather than consuming large amounts at once. This approach helps keep the body hydrated without overfilling the stomach, reducing discomfort. Avoiding sugary or carbonated beverages is also recommended, as these can increase gas and bloating.
Practicing mindful eating is another effective way to manage side effects. Eating slowly, chewing food thoroughly, and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues can prevent overeating, which can otherwise strain the stomach and lead to acid reflux. Mindful eating helps patients build a balanced relationship with food, a crucial component for long-term weight management.
Final Thoughts
Managing side effects after a gastric balloon procedure involves a combination of dietary adjustments, regular follow-ups, and mindful eating habits. By understanding and implementing these practices, patients can minimize discomfort and maximize the benefits of their gastric balloon. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers are key steps toward a successful, smooth recovery.
At Med Expert Clinic, we specialize in guiding patients through every step of their weight loss journey with non-surgical solutions like the gastric balloon. Our team provides expert support, helping patients feel confident and comfortable throughout the process.
Ready to start your journey? Contact Med Expert Clinic to learn how our expertise can support you in achieving a healthier, balanced life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common side effects of a gastric balloon?
The most common side effects of a gastric balloon include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, acid reflux, and bloating. These symptoms are typically most intense in the initial days after placement as the body adjusts to the balloon. Most side effects decrease with time and can be managed with dietary adjustments and hydration.
How can I manage nausea caused by a gastric balloon?
Nausea is a frequent side effect after gastric balloon placement. To manage it, try eating small, bland meals and avoid rich, greasy foods. Staying hydrated with small sips of water can also help, as can drinking ginger or peppermint tea, which may soothe the stomach. If nausea persists, consult your healthcare provider for potential anti-nausea medications.
When should I seek medical attention for side effects from a gastric balloon?
Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, ongoing vomiting, fever, or signs of infection such as chills or worsening abdominal pain. These symptoms could indicate serious complications that require prompt medical assessment. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if these symptoms occur.
Can the gastric balloon deflate or move out of place?
Yes, in rare cases, the gastric balloon can deflate and migrate through the digestive tract. This can lead to a blockage, causing intense pain or vomiting. Watch for symptoms like severe abdominal pain or a general feeling of being unwell. Contact a doctor immediately if you suspect deflation or migration of the balloon.
How often should I have follow-up appointments after gastric balloon placement?
Regular follow-up appointments are essential for monitoring your progress and managing any side effects. Typically, appointments are scheduled within the first few weeks after placement and continue periodically throughout the duration the balloon is in place. Your healthcare provider will establish a schedule that meets your needs to ensure a smooth and safe experience.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.